Demystifying Google Analytics 4 User ID Tracking: A Comprehensive Guide

Ever wondered how long Google Analytics 4 (GA4) stores information about your users and their activity? Understanding data retention is crucial for getting the most out of your analytics. This guide dives deep into GA4’s data retention settings, explaining what data is affected, how long it’s kept by default, and how you can customize it for your needs. We’ll cover the difference between event and user data retention, explore the “reset on new activity” option, and ensure you have the right controls in place to analyze user behavior effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Understand GA4 Data Retention
- Types of Data Retention
- Event and User Data Retention Explained
- Event Data Retention Period
- User Data Retention Period
- Reset on New Activity Option in Data Retention
Understand GA4 Data Retention
GA4 lets you control how long it holds onto user data. By default, this is set to just two months. This might be enough for basic daily reports, but for deeper dives and historical comparisons, you’ll want to extend it. The good news is you can stretch it all the way to 14 months! This allows you to analyze trends, compare past and present performance, and make more informed predictions.
Types of Data Retention
There are two types of data retention which is provided by GA4 and they are mentioned below:
- User Retention
- Event Retention
Let’s explore the both Retention.
Event and User Data Retention Explained
The retention period you set in GA4 applies to several key areas:
- User-level data: This includes details about individual users tied to cookies, user IDs (like User-ID), and advertising identifiers (e.g., DoubleClick cookies, AAID, IDFA).
- Event-level data: This refers to information about specific actions users take on your site or app.
In essence, you control how long GA4 keeps this user-specific information before it’s automatically deleted.
Important Exceptions:
- Google Signals data: This data from signed-in Google users has a maximum retention period of 26 months, regardless of your settings.
- Default signed-in user data: By default, signed-in user data also expires after 26 months. However, if you set your GA4 retention to a shorter period, the signed-in user data will also be deleted sooner.
Heads Up: Limited Tracking for Demographics in GA4
While you can control how long GA4 stores most user data (events, user details), there’s an exception for specific user demographics. Information like age, gender, and interests is automatically deleted after:
- 6 months for Universal Analytics properties
- 2 months for GA4 properties
This means this data won’t be available for analysis after that timeframe if a user hasn’t returned to your site or app within that period.
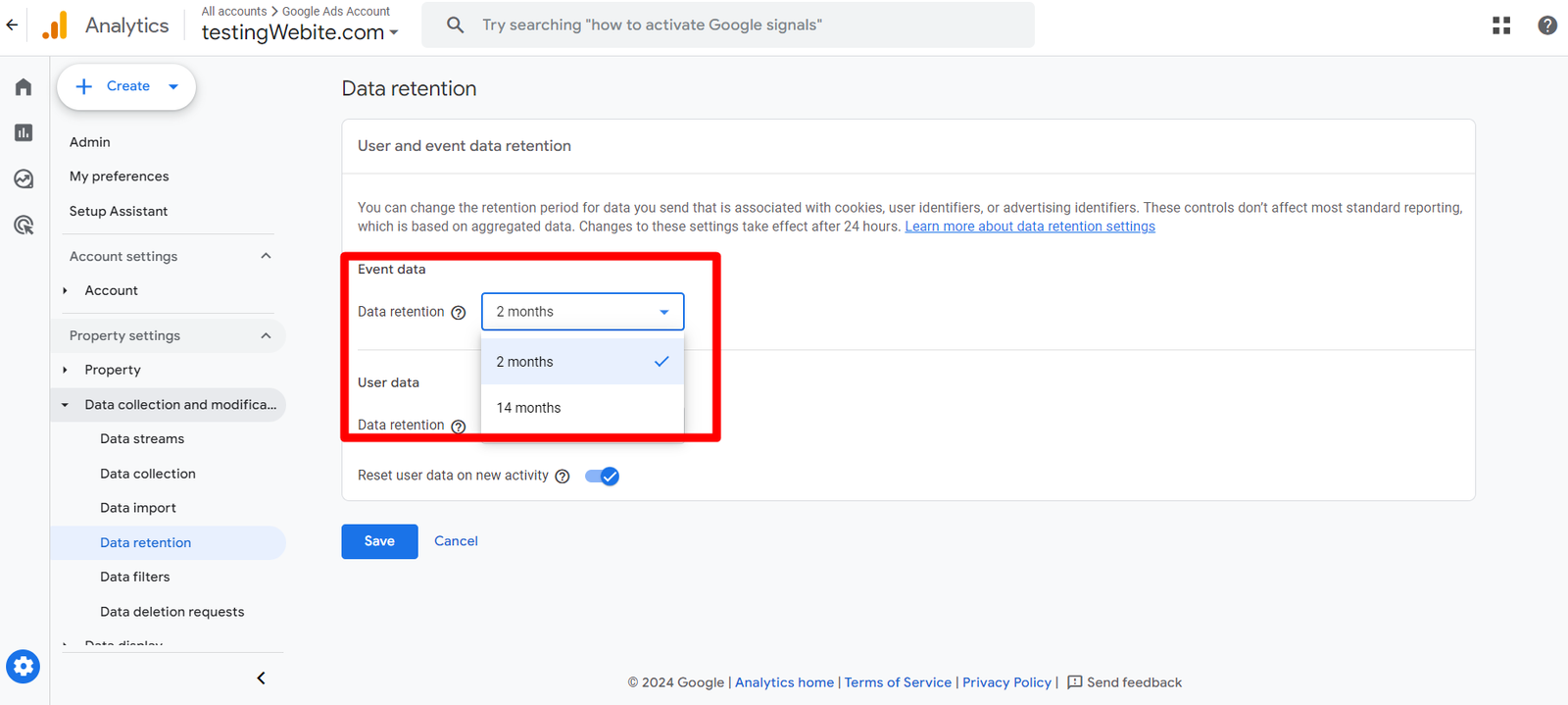
Event Data Retention Period
In Google Analytics 4, you have able to change the retention period in two ways: For 2 months and For 14 Months.
User Data Retention Period
In Google Analytics 4, you have able to change the retention period in two ways: For 2 months and For 14 Months.

Reset on New Activity Option in Data Retention
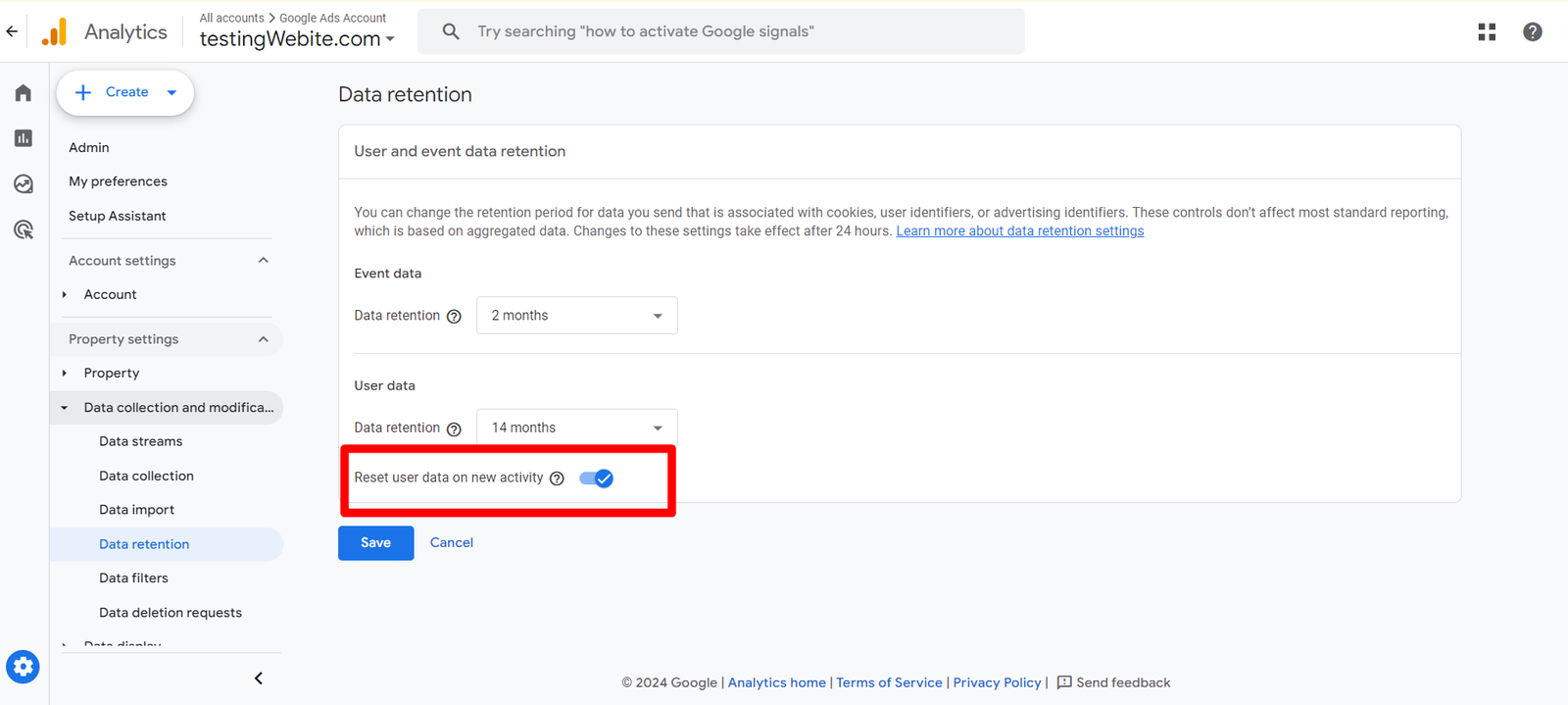
Imagine you set your GA4 retention to 14 months. This means user data gets deleted after 14 months of inactivity. But what if a user visits your site every month? Here’s where “Reset on new activity” comes in:
Turn it ON: With this option enabled, any new activity from a user (like a visit or event) resets their retention clock to the current date + your chosen retention period (14 months in our example). So, if a user visits monthly, their data never gets deleted!
Turn it OFF: If you disable this option, user data gets automatically deleted after the set retention period, regardless of their activity.
Key Points:
- This feature only affects user-level data, not event-level data.
- It essentially lets active users extend their data lifespan within GA4.
In Short: Turn “Reset on new activity” on to keep user data fresh as long as they keep interacting with your site or app!
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding data retention in Google Analytics 4 is important for businesses to make informed decisions based on accurate and relevant data. By default, GA4 only stores user data for two months, but this can be extended to 14 months for a more complete historical picture. This extended retention applies to both user-level data (like user IDs) and event-level data (specific actions users take). To maximize your data insights, especially for inactive users, consider enabling the “Reset on New Activity” option. This ensures user data stays relevant as long as they keep interacting with your site or app. Remember, longer retention allows for better trend analysis and informed decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is data retention?
Data retention refers to the length of time that data is stored and available in a system or database. In the context of Google Analytics 4, it determines how long user-level and event-level data is retained in the property.
Why is data retention important?
It is important because it affects the availability of historical data for analysis and reporting. It allows businesses to understand trends, track user behavior over time, and make data-driven decisions based on past performance.
How do I choose the right data retention period?
Choosing the right period depends on factors such as regulatory requirements, business objectives, and data storage costs. It’s important to balance the need for historical data with privacy and compliance considerations.
What are some considerations for data retention?
When deciding on settings, consider factors such as data privacy regulations, storage costs, historical analysis needs, and the impact on data-driven decision making. It’s important to find a balance that meets both business and compliance requirements.
Connect with Us
Stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of marketing technology by connecting with Advaana Inc. Let's work together to transform your marketing technology landscape. Connect with us today and take the first step towards achieving your MarTech goals. image

(717) 461-9080